Development Platforms MURO

TurtleBots
The MURO lab utilizes TurtleBots created at Clearpath Robotics. Turtelbots are the ground robots in our testbed. They are useful for verifying control algorithms performance on hardware.
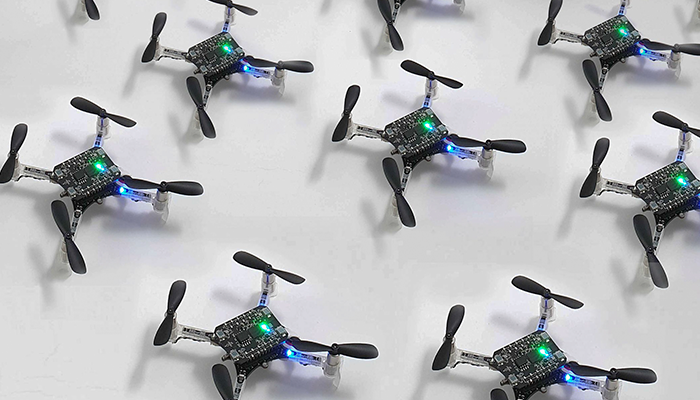

Crazyflies
The lab also currently utilizes Crazyflie 2.1s created at Bitcraze. Crazyflies are micro quadcopters. They are useful for testing swarming and cooperative task solving operations.
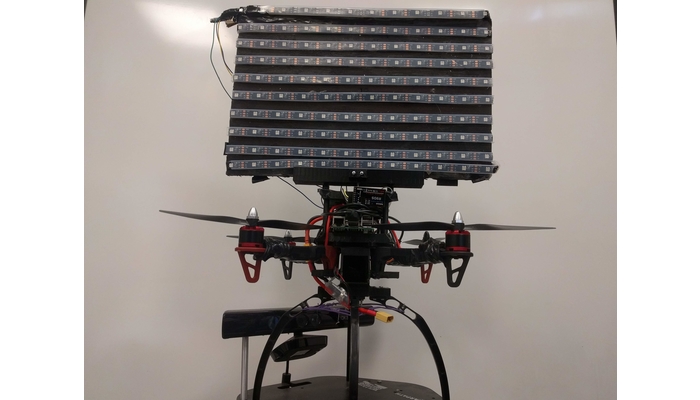

MuroCopter
Here you can check out the in-house development of drones with the goal to implement distributed algorithms. [Video]
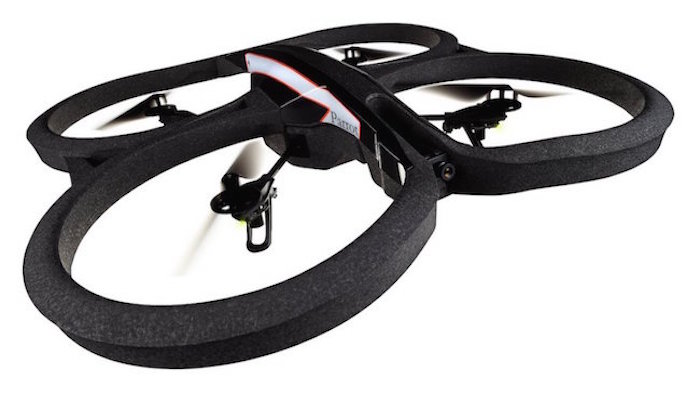

Parrot AR2 Drones
This section explores our usage of Parrot drones. These drones are used for testing various multi-agent robotic algorithms under relaxed dyanmic constraints.
Localization MURO
Aerodrome
The MURO lab utilizes ultrasound beacons created at Marvelmind. The beacon set provides indoor positioning for navigating turtle bots.
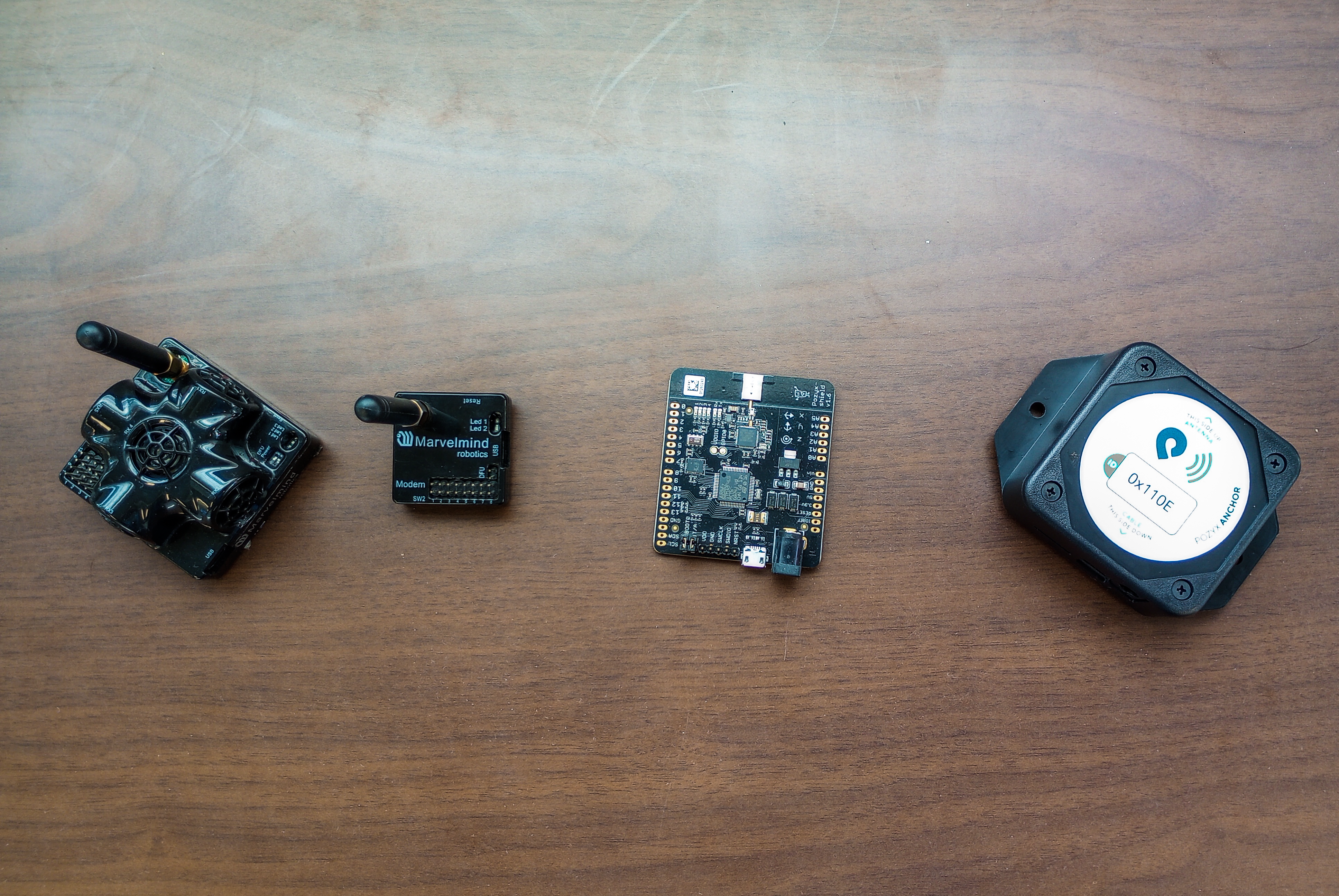
Ultrasound and Ultra Wideband Beacons
The MURO lab utilizes a variety of beacon positioning systems created at Marvelmind and Pozyx. These beacons provides indoor localization for navigating turtle bots.
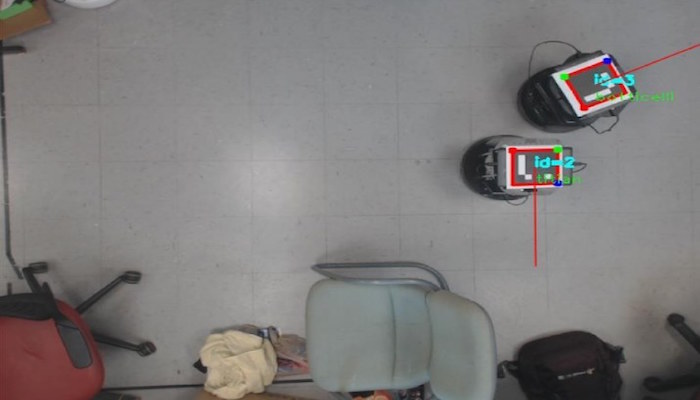

Top-Mounted Cameras
This section explores our use of hardware and computer vision algorithms in relation to localization. The role of the localization subsystem is to provide state estimates of agents to the larger system.

SLAM
Here you will find an expalnation of Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, which is otherwise known as SLAM. In short SLAM consists of a robot building of a map of its surroundings using an estimate of its location while simultaneously estimating its location using the map of its surroundings.

Onboard Localization
ORB-SLAM allows us to do what is sometimes difficult in the world of robotics - onboard localization. Read this section to find out more.
Human Interaction MURO

Android App
The MURO lab utilizes an android tablet application as a tool for human-swarm interactions. Our android application uses ROS in order to communicate each of the active robots in the multi-agent network. This section explains the different applications where the app is useful.
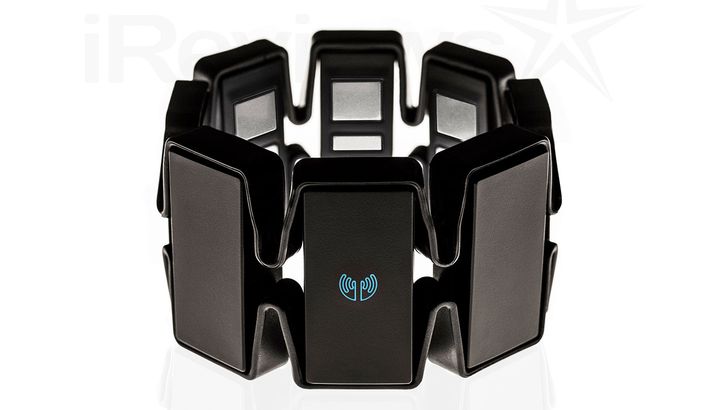

Myo armband for EMG signals
The MURO lab uses a Myo armband for encoding Robot inputs via muscle movements in human arm. The signals are decoded via Hidden Markov Models and are used to fly drones.
Related Software MURO

Robotic Operating System
Here you will find an explanation of ROS. The open source ROS has been chosen as the software platform to enable the network structure, relying on a publisher-subscriber model to allow for inter-robot communication and coordination.
Implementations MURO
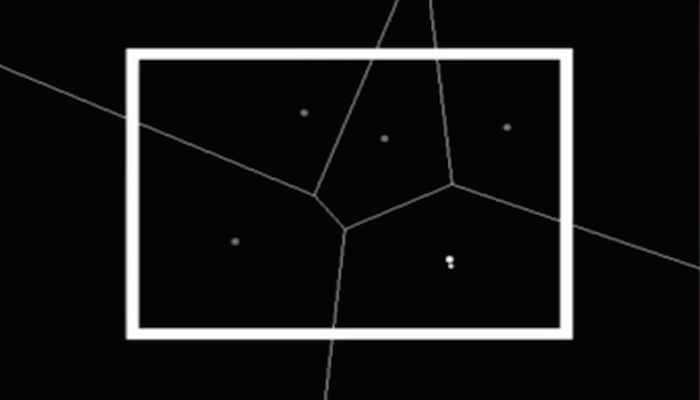
Multi-Agent Coverage Control
The purpose of multi-agent coverage control is to direct agents (robots) to cover a space as best they can. In this section you will find information on how Voronoi Diagrams are being used by the MURO lab for coverage control. Fortune's algorithm is also highlighted as a principle piece of the coverage control algorithm along with other centroid finding algorithms.
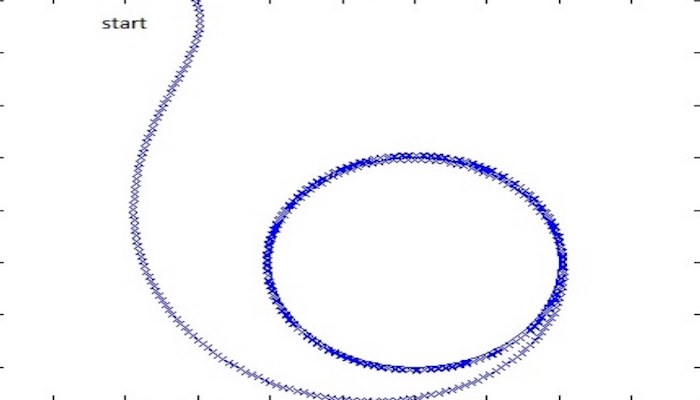
Cyclic Pursuit
"Global Path Following for the Unicycle and Other Results" by Mohamed I. El-Hawwary and Manfredi Maggiore, provides a robust method for unicycle (TurtleBot) dynamics. Open this section to find our more.